Recommended
In this user guide, we describe some of the possible causes that the Microsoft DFS client can cause, and then provide possible recovery methods that you can use to try to resolve the issue. g.Distributed File System (DFS) is probably a collection of client and server tools that enable an organization using Microsoft Windows servers to organize many SMB distributed shares into a distributed file system.
g.Distributed File System (DFS) is a client-server service agreement that allows an organization running Microsoft Windows servers to organize multiple SMB distributed file shares into a single distributed file for the system. It is also referred to as “MS-DFS” or “MSDFS” in any context such as a Samba user area or a room project.
g.Distributed File System (DFS) is a set of client-server services that enables a vendor using Microsoft Windows servers to push multiple SMB distributed file shares directly to a distributed file system. It is also referred to as “MS-DFS” after “MSDFS” in some contexts, such as in the current Samba user space project.
g.
- 2 minutes to read.
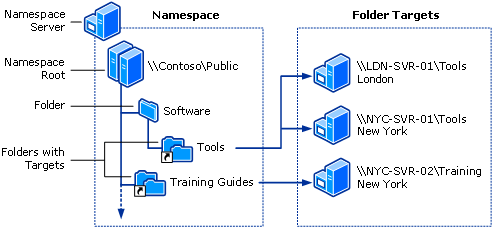
Distributed File System (DFS) features provide the ability to logically group shared resources across multiple servers and immediately and transparently associate shared resources with a single hierarchical namespace. DFS configures resources that are shared on the network in a tree structure only.
DFS supports stand-alone DFS namespaces with one host machine and domain namespaces with two or more host servers and high availability. DFS topology data for domain namespaces is considered to be stored in Active Directory. Data includes DFS root, DFS links, and DFS targets.
Each pageA DFS specification framework has one or more root targets. The root target is the provider, the server that is running the DFS service. The DFS tree will provide you with one or more DFS connections. Each dfs link points to one or more shared folders on the network. You can add, modify, that is, remove DFS links from the DFS namespace. If you delete the last destination associated with a DFS web link, DFS will delete the DFS link found in the DFS namespace. (In previous entries, DFS links were referred to as jct dots.)
The DFS link can probably point to a different shared folder; versions are called targets. When users enter a DFS link, the DFS node selects a set of destination types for the client’s location information. The shopper goes to the first available destination in the set. Helps align client requests across functional targets and can continue to provide users with easy access even if some computers fail.
- Add a DFS link to the great DFS root.
- Create or delete standalone and simple domainsdfs namespaces.
- Add targets to an existing awesome DFS link.
- Remove the DFS connection from the DFS root.
- Remove agreement with DFS link.
- View and configure DFS root and link information.
For a list of DFS attributes, see Distributed File System Features .A
For a list of DFS structures, see Distributed File Systems .
Targets running Microsoft Windows can now be published to the DFS namespace. You can also publish any existing third-party shares that can be accessed by client forwarders in the DFS namespace. However, unlike a server-hosted share that must be running Windows Server, they cannot host any type of DFS root or provide you with links to other DFS targets.
DFS requires Windows Server File Replication to simulate changes between replicated targets. Users may want to modify files in a specific repository, and the file replication service otEdits changes to other discoverable destinations. The service saves most of the changes made to the document, and sometimes to files.
Recommended
Is your PC running slow? Do you have problems starting up Windows? Don't despair! Fortect is the solution for you. This powerful and easy-to-use tool will diagnose and repair your PC, increasing system performance, optimizing memory, and improving security in the process. So don't wait - download Fortect today!

This article explains how Microsoft creates DFS. For a general discussion of the concept and other implementations, see Distributed File System.
Distributed File System (DFS) is a fixed server services client that enables a charity using Microsoft Windows servers to manage multiple distributed SMB file shares on a distributed file system. DFS has two components: site transparency (via the namespace component) and redundancy (via the file replay component). Together, these components ensure data availability in the event of a failure and / or high load by realistically grouping shared resources with multiple different locations into a single folder, our own “DFS root”.
Microsoft DFS is interchangeably referred to in the marketplace as “DFS” and “Dfs” from Microsoft and is not related to DCE Distributed File System, which is usually trademarked “DFS” [1] but was discontinued in 2005.
It is also referred to as “MS-DFS” with “MSDFS” in some contexts, such as from the Samba User Space project. [2]
Presentation
You may not need to use two additional DFS devices together; It would be perfectly possible to use the large namespace component without DFS directory replication, and it would be perfectly reasonable to replicate files between computers without merging them into a namespace.
DFS root can only be installed through a server version of Windows (from Windows NT 4.0 and up) and therefore (in the opensolaris [3] kernel space), or on a good reliable Samba machine ( in a more user-friendly storage). Windows Server Enterprise and Datacenter editions can host multiple DFS root files on the same server. OpenSolaris stands for support for multiple DFS root systems in a “future project based on the DFS Active Directory (AD) domain namespaces.” … [4]
- Standalone DFS Namespace – Allows a single DFS to exist only directly on the local machine and thereforeAlso, do not use Active Directory. Standalone DFS can only be accessed from the computer on which it is normally created. It is not fault-tolerant and cannot be attached to any other DFS. This option is only available on Windows NT 4.0 Server systems. DFS standalone roots are rare due to their limited usefulness.
- domain namespace / stores the DFS configuration in Active Directory, making the root of the DFS namespace at
\
, optionally
How do I enable the distributed file system in DFS client?
Open From Server Manager, select Manage -> Add Roles, not to mention features.Click Next to start the program.Select a role-based or feature-based installation.Select a server.The next section is the server roles in the file and storage utility.Click Next twice to confirm and install the applications.
\
available is. Namespace roots can connect to a domain controller or sector member server. While domain controllers will certainly be used as the actual namespace server, multiple member servers should only be used to fully determine the implications of admission.
DFS Namespaces
What is DFS and how does it work?
Distributed File System (DFS) capabilities allow you to logically group stock options across multiple servers and seamlessly link shared resources into a single hierarchicalth namespace. DFS organizes shared resources on a network using a tree structure.
Traditional file shares associated with a disconnected server have SMB paths that begin with the
form. connected
\
Domain-based DFS boot share paths differ in that the domain name is the basebut on the server name in
\How does Microsoft DFS work?
DFS uses most Windows Server File Replication Services to replicate changes between replicated targets. Users can modify files stored at a specific destination, and file replication support propagates changes to additional designated destinations. The service stores your last capture or file changes.
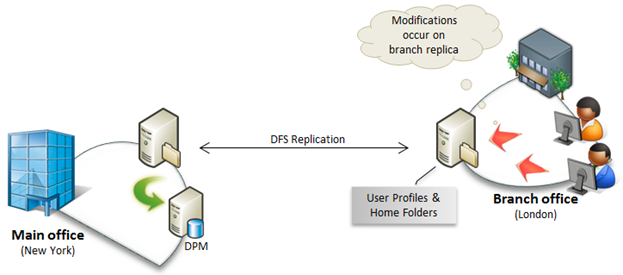
When a user accesses a Share directly or by mapping a drive, their computer can access any available host connected to that Share, in accordance with the laws set by that network administrator. For example, by default, users select the server closest to them; However, this can be changed to take advantage of a specific server.
If a server goes down, the client can transparently select any number of different servers for the user. An important caveat about this flexibility is always that currently open files may become unusable because open files cannot be switched.
DFS Replication
Early versions of DFS. The File Replication Service (FRS) used by Microsoft typically provides basic file replication functionality for midrange servers. FRS changed the identified or original files and copied the latest version of the entire file to each ofservers.
“DFS Replication” (DFSR) is configured in Windows Server 2003 R2, which improves FRS by copying only portions of all files that have changed (remote differential compression) using data compression to make sure you reduce network traffic and providing administrators with flexible configuration options to reduce network traffic on a simple schedule
History
What are the requirements for DFS?
No additional personal hardware or software configuration is required to perform DFS administration or use DFS namespaces. A namespace server is a space controller or member server that hosts each namespace. The number of namespaces that you can host on a server is determined by the operating system running on all namespace servers.
DFS was first introduced as an add-on to Windows NT 4.0 Server, often referred to as “DFS 4.1,” [5] , and has since become a standard component of Convenience Editions. Windows 2000 Server.Client support is included in Windows NT 4.0 and later.
Linux 2.6.14 and later kernels [6] contain an SMB VFS client called “cifs” that supports DFS.
How do I enable DFS client?
First open Server Manager.Select Next from the Before You Begin menu.From the Installation Type menu, select Role-Play or Role-Play.
On Mac X os, DFS is clearly natively supported on Mac X 10.7 (“Lion”). [7]
Specifications
There are a number of DFS related specifications. They are available through the Microsoft Open Specifications: [8]
- [MS-DFSC]: Distributed File System (DFS): Reference Protocol
- Defines All Distributed File Systems (DFS): A reference protocol that allows file system clients to resolve names from a namespace that is sold on many servers and regions within local names on some registry servers.
- [MS-DFSNM]: Distributed File System (DFS): Namespace Protocol
- Defines Distributed File System (DFS) management: a namespace management protocol that provides a powerful RPC interface for managing DFS configurations. The server has always been a DFS service that uses support for this RPC to manage DFS.DFS
- [ms-dfsrh]: Replication support protocol.
- Defines the DFS Replication helper protocol, which is a distributed component object model (DCOM) interface configuration for configuring and monitoring the DFS Replication helper protocols on your server.
See Also
- List of Microsoft Windows Components
- Comparison of DFS
Links
Ext th Links
- How DFS Works: Remote File Systems
How do I enable DFS client in Windows 10?
Click Start, select Administrative Tools, and then click DFS Management.In the console tree under the Namespaces node, right-click the folder containing the targets and select Properties.If you are declining referrals, check the Return Customers box to help you choose your preferred referrals.
How do I enable DFS client?
Open the Dispatcherp servers to get started.From the Before You Begin menu, select Next.In the Installation Type menu, select Install by Role or Feature.
How does Microsoft DFS work?
DFS uses the Windows Server Data File Replication Service to replicate changes, for example, between replicated targets. Users can modify documents stored in one destination, and often FRS propagates the hesitation to other specified destinations. The service saves the last update of a document or file.
How do I enable DFS client in Windows 10?
Click Start, go to Administrative Tools and suspend DFS management.In the console tree, just below the Namespaces node, right-click the directory containing the targets and select Properties.On the Referrals tab, click the Search box for Preferred Customer Service.
How can I share folder in Windows 10?