In this article, we will learn about some of the possible causes that could cause the BIOS to change the processor multiplier, and then suggest possible fixes that you can try to fix the problem.
Recommended
g.Turn on your computer and click the Organize BIOS button to enter the BIOS.Find the “Processor Speed” setting in the BIOS menu.Select the “Processor Speed” setting and optimize the value to the next below the specified setting.Save and exit BIOS.
How To Lower The Processor Frequency By Using The FSB Clock Speed
How To Reduce CPU Speed By Using A CPU Multiplier
How do I change my CPU multiplier?
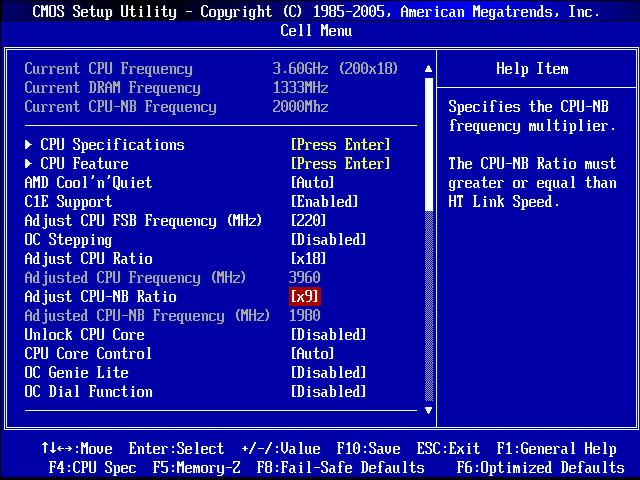
Increase the multiplier In the Overclocking Settings menu, use the down arrow to navigate to CPU Ratio or similar and thus highlight the current climate. If If this is your first time doing this, try increasing the multiplier by one. If you have a 3.3 GHz wall clock for the model, the multiplier will be set to 33.
Too fast orComputer processors that are too hot can certainly slow down their speed due to a technique called “underfrequency.” Depending on the motherboard and processor, there may be special controls in the device BIOS that experts say regulate the bus speed on the motherboard and the processor multiplier. The FSB speed multiplier and processor characteristics form the basis for setting the processor speed. Advanced users can increase the speed of the processor using a similar method called overclocking. Overclocking and overclocking work on the same issues. However, some processors and motherboards block the processor speed, so it cannot be adjusted.
In addition to the computer, activate the most important BIOS setup item to boot the BIOS.
Look in the BIOS menu for the “Processor Speed” setting. Option name and position differ depending on equipment. The parameter is usually recognized in the Advanced submenu. The preliminary name contains a combination that is associated with the words “FSB”, “Clock”, “CPU”, and sosame “Frequency” in the title.
v
Select the “Processor Speed” option and replace the value with the next lower value with numbers. For example: the default cpu frequency of 266 MHz will be left to remove the next lower packet setting in the list, which is 233 MHz.
How do I change the CPU multiplier in BIOS?
Turn on your computer and press the BIOS setup button to enter BIOS.Look in your BIOS product for a suggestion for setting “Processor Speed”.Select the “Processor Speed” option and also change the value to the next lower option.Save BIOS and exit.
Turn on the computer, press the BIOS setup button to start the BIOS.
Recommended
Is your PC running slow? Do you have problems starting up Windows? Don't despair! Fortect is the solution for you. This powerful and easy-to-use tool will diagnose and repair your PC, increasing system performance, optimizing memory, and improving security in the process. So don't wait - download Fortect today!

Look in some BIOSes for menus with the “CPU Multiplier” or “CPU Ratio” setting option. The location setting differs depending on the equipment, but is always found in the Advanced submenu. The parameter name can contain additional function statements in the header, for example “Clock”.
Select “
one of our “CPU Multiplier Clock” options in addition to changing the value for a future option with a lower number. For example: if the market has a standard multiplier of 16, it should be reduced to 15 for you.
Dan Stone started creating in 2006, specializing in education, technology and music. He is a good web developer for a communications employer and has previously worked in television. Stone got sta bachelor’s degree in journalism nearby and a master’s degree in communications from Northern Illinois University.
- The BIOS setup key is computer dependent. The start screen usually provides a key with the message “Settings” in the accompanying phrase. However, if the screen does not display any keys, it is usually F1, F2, F8, F12, Esc, or Del.
- If everyone boots up and sees that the processor is still running incredibly fast, you can rerun the FSB slowdown and multiplier reduction analysis. The FSB multiplier and locations can be safely reduced to these minimum settings. If you clear a parameter that is being written one value at a time and start to go beyond it, you can check the stability of the software and see how low that particular value can get before you have any usability issues.
- Processor speed is actually calculated by multiplying the FSB clock speed by the average processor multiplier.
- When people set the FSB frequency or CPU multiplier higher, not lower, there is the risk of overheating in addition to breaking the computer. Lowering the frequency does not greatly increase the risk of damaging the processor; relatively safe to help with overclocking. If you set the FSB wake or CPU multiplier too low, I would argue that the computer could drop to unused power levels. If your computer can become unusable due to a change you are resetting, you can reset the BIOS to default settings if desired, either by using a BIOS setup or by removing the backup battery from the computer.
Does changing CPU affect BIOS?
You also don’t need to do anything in the BIOS if you just swap the processors at boot right to the desktop. On some systems, a screen is displayed informing you that due to the return to hdwr, you need to enter BIOS. On first launch, you just need to save the running settings and return to the desktop.
BIOS (Basic Input / Output System) is software that is installed on your motherboard and loaded before the operating system. It provides a Where interface that you can use to frequently configure your hardwareInstalled on the motherboard. Since you can change parameters such as voltage and frequency in the BIOS, you can use a manual overclocking device to increase alarm rates and possibly improve performance.
It is assumed that you have a basic understanding of what overclocking is and how it is easiest to do it. If you’re new to overclocking and want to learn more about the basics, check out the Overclocking Types to Get Started and Accelerate sections.
You also need to make sure you have the right stuff. Try it
How do I change my CPU multiplier?
Increase the multiplier In the Overclocking Settings menu, use the Down arrow to navigate to CPU Ratio or similar and remember the current setting. At the first moment, try increasing this particular multiplier by one. For example, if you have an alarm rate of 3.3 GHz, the multiplier would be 33.
Before overclocking your BIOS, think about software options that will simplify the process. The Intel® Extreme Tuning Utility (Intel® XTU), for example, is an easy-to-use option for people new to overclocking. An even simpler automated option that works with the latest Intel® Core ™ processors is the Intel® Performance Maximizer (Intel® PM), which you can read in detail about here.
How do I change my CPU core ratio?
Enter BIOS. The first step in overclocking is pressing the Delete key to enter the MSI Click BIOS.Press F7 to go to advanced mode.Go to OC settings.Adjust the CPU utilization rate and ring rate.Adjust the processor core voltage.Disable Intel C-State (C-State)Full!
On the other hand, overclocking from BIOS often provides the most complete access to everything provided system performance parameters. If you need to manually tweak the system and handle all aspects of your own overclocking, it must be BIOS related.
Please update your BIOS to the latest available version before starting. This way, you can take advantage of any new features or enhancements released by your motherboard manufacturer. Check your motherboard online or refer to your motherboard documentation to find out how to properly update your BIOS.
The appearance of individual BIOSes depends on the motherboard manufacturer. To access the BIOS, you need to switch to a specific key, for example. See the documentation that came with your motherboard for specific instructions. Clock

Changing the frequency or voltage may void the product warranty and reduce the stability, safety, performance, and life of this processor and other components.
Whenever you change your BIOS settings, make them as small as possible. Then apply the changes to your system system and run the test. Not only will this obviously tell you that you are making settings that have a particular overclocking advantage, but it will also allow you to easily fix any build that results in an unstable system. In most BIOSes, you can save your settings as profiles. Every day you see that a good combination of these parameters results in balanced overclocking. Save it as a report for easy replication.
Whenever you change your BIOS settings, adjust in the smallest easy steps. Then apply the changes to your system system and run the test. Not only will this tell you that the change will overclock your precious resource, but it will also tell you that you can probably easily fix any ringer settings that are causing the console to become unstable. Most BIOSes allow your settings to be used as profiles. Either way, you find a good combination of settings that results in a fixed overclock, save it as a consumer profile for easy replication.
Speed up your PC today with this easy-to-use download.How do I change my CPU core ratio?
Enter BIOS. The first step in overclocking is to help you hit the Delete key on a very important BIOS click from MSI.Press F7 to select advanced mode.Go to OC settings.Adjust the CPU utilization rate and ring rate.Adjust the processor core voltage.Disable Intel C-State (C-State)Full!
How do I change the CPU multiplier in BIOS?
Turn the computer over and press the BIOS setup button to enter the BIOS.In the BIOS menu, find the “Processor Speed” setting option.Select the “Processor Speed” option and replace the treasure with an idea with the next lower number.Save and exit BIOS.
How do I change my CPU multiplier?
Increase the multiplier In the Overclocking Settings menu, use the arrow below Control to navigate to the CPU Ratio record, or perhaps a similar heading, and make a note of the current match. If this is your first time doing something specific, try adding it to a multiplier. For example, if you have a 3.3 GHz clock speed, the specific multiplier will be set to 33.
How do I change my CPU core ratio?
Enter BIOS. The first step to revert to overclocking is to hit the Delete key to enter the MSI Click BIOS.Press F7 to go to advanced mode.Go to OC settings.Adjust the CPU utilization rate and ring rate.Adjust the processor core voltage.Disable Intel C-State (C-State)Full!