Recommended
Over the past few days, some users have encountered a known Linux formatting error with the FAT32 file system. This problem can arise for several reasons. Let’s discuss this now. g.To format a partition with any FAT32 file system, you need to use “mkfs mkfs”. On computer operating systems, mkfs is a command used to associate a block storage device with a selected file system. The team is part of Unix and Unix-like operating systems. https://en.wikipedia.org ›RSS feed› Mkfs mkfs – Wikipedia ”and specify the FAT32 file system. Run lsblk again with the -f option to make sure your changes are written to disk. You can mount your own newly created partition using the “mount” command.
What format should USB Stick be for Linux?
Perhaps the most common file systems are exFAT and NTFS on Windows, EXT4 on Linux, and FAT32, which can be used on all operating systems. We will show you how to format a USB stick or SD card to FAT32 or EXT4. Use EXT4 if you plan to use your disk only on Linux systems, otherwise design it with FAT32.
Linux is a stable and extremely powerful operating system that is very popular in the community. Thanks to open source and free source, Linux is growing rapidly, reaching a large audience of users. The beauty of Linux is that it offers the perfect variety of tools with the features mentioned, and now it’s the same with formatting our USB stick.
There are some great technologies that allow Linux users to easily format their USB files, which can be categorized into command line category or whole GUI category.
Besides some, there are several file systems that can be formatted on a USB stick. For our USB hardware to have maximum compatibility with additional peripherals, FAT32 is what you need.
Recommended
Is your PC running slow? Do you have problems starting up Windows? Don't despair! Fortect is the solution for you. This powerful and easy-to-use tool will diagnose and repair your PC, increasing system performance, optimizing memory, and improving security in the process. So don't wait - download Fortect today!

So, in this guide, we are definitely discussing how to easily format your USB sticks FAT32 drives in Linux.
Format Your USB Stick
Can Linux format NTFS?
Linux proves its versatility by promoting all storage formats supported by Windows. This makes NTFS a better option, and fortunately on Linux, it’s easy to format a problematic hard drive to NTFS. There are many ways to do this, except that GParted is one of the easiest.
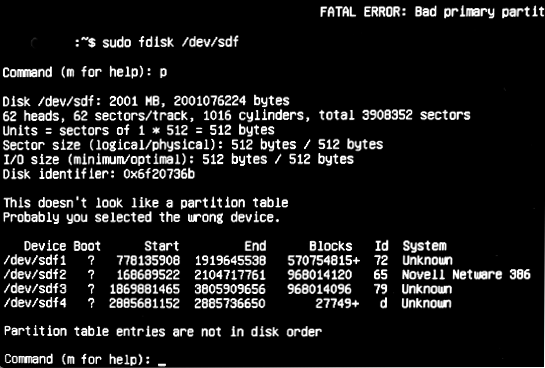
Before we start formatting our USB device, my wife and I need to find it. This can be done by simply typing the following command in a specific terminal:
In my case, this is a device located in a rectangular area (/ dev / sdb /):
How do I format my device to FAT32?
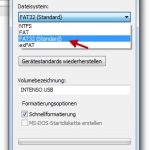
Connect the USB storage device to your computer.Open Disk Utility.Click Return to select the USB storage device in the specific left pane.MoreClick to go to the “Delete” tab.In the Volume Format: selection box, press. MS-DOS file system.Click Remove.In the current confirmation dialog box, click Delete.Close the Disk Utility window.
Now that we have found your device, let’s move on to the main process, where among the huge set of tools Linux has to offer, we have to look at two ways in which users can format their USB data in Linux.
Formatting USB Stick Installation With GParted
GParted is a partition editor primarily responsible for creating and monitoring hard disk partitions, including repartitioning and deleting partitions.
a) Install GParted
First, we need to install GParted on our Linux systems, which is done by entering the on command in a terminal:
Of course, to make sure it’s installed, you just have to do it by running the following command:
b) Remove your data by adding zeros (optionalbut)
The next step has always been to completely erase all hardware present on your USB device so that it cannot be restored with a recovery tool in the future. However, this is an optional step and you can skip it if you like. However, for security reasons, this is highly recommended for anyone doing it. This process can be accomplished by running the following command in a terminal:
Here you need to return the part of / dev / sdb that will be returned after = ends with the destination created by your USB device that you specified earlier.
c) Create and format your USB device
Now we have finally come to the heart of the process. First, we need to carefully unmount the USB device / dev / sdb1 (use the location above) on your systems, as we cannot format the mount device. This can be done with the following command:
Next, we are probably going to create a new partition table, in which we should also mention any type of partition table, which many ofyou want. In our case, it could be msdos. To do this, simply run the following command in a specific terminal:
Now we need to create our own section in which we specify the type of section, the application file that our USB device should be, and the size that our section should be larger than. In our case, we want our USB device to have the FAT32 file system, the sorting of the primary partition, and the full USB height of our partition. This can be done using the keep with command:
After that, we can finally format our USB device to FAT32 using the mkfs command, which usually looks like this:
Note that we are using the / dev / sdb1 location here instead of the current / dev / sdb location we used earlier. This is because we don’t want some of our device’s memory to be formatted here.
Can you format to FAT32?
Enter [This PC] in the Windows search bar and search for [This PC], then select the [Open] check box ②. Right click on the broken USB stick, then select [Format] ④. Select the file system in [FAT32] ⑤, then click [Start] ⑥. Click [OK] ⑦ to start formatting the USB stick.
To make sure your device is partitioned correctly, run the command here to print the partition table:
And voila, this is where the whole scene ends. You will now find your fully formatted USB devicesO. Your
Format USB Hard Drive
For users who want a more easy GUI experience, Disks is actually a disk management tool that can be preinstalled on Ubuntu and almost any other Linux system. To open this one, just find it in the main panel and click on it when the name appears.

After the disc function is open, first select your device you want to format on from among the most available ones displayed in the disc application. In my case, it will definitely be:
Click here on the gear below the Volumes section, then select Format Partition from the options provided.
After selecting this option, a window will open asking you to enter a new name for the partition and the type of your file system. Since we want the desired device to support the FAT file structure, we choose the following:
Then enter your contact details and when you are absolutely sure everything is in order, click the “Format” button on the righthome page as shown by the pointer in the image below.
And bam !, this is where the whole process ends. You will now find your fully formatted USB device.
Conclusion
As the above methods show, formatting USB drives in Linux is an extremely simple process. All you have to do is plug in the device and the type of file you want and just run a command on a terminal or use the Disks utility to format your corporate device. Of course, there are several other tools you can use to format USB devices, but these should be reserved for the Destiny tutorials.
Can I format FAT32 on Linux?
To format a section usingBecause of the excellent FAT32 filesystem, you must use the mkfs command and specify the new FAT32 filesystem. Re-run lsblk and the -f option to indicate that your changes have been written to disk. You can mount your new favorite partition, usually with the “mount” command.
$ sudo parted / dev / sdb –script – mkpart Primary fat32 1MB 100%
Speed up your PC today with this easy-to-use download.How do I force a FAT32 format?
Click on the start menu.Click This PC.Right click your USB stick.Click Format.Click Start. If the file process is not listed as FAT32, click the dropdown menu and make a decision.Click on OK.Wait for the player to format the file, then click OK to complete the process.
How do I format my USB drive to FAT32?
Connect a USB storage device to each computer.Open Disk Utility.Click here to select your USB storage device under Remaining Permitted.Click to go to the Delete tab.In the Volume Format: selection box, press. The MS-DOS file system.Click Remove.In the confirmation dialog, click Delete.Close the Disk Utility window.
Can I format FAT32 on Linux?
To design a FAT32 partition you need to use the one person mkfs command and specify the FAT32 file system. Run lsblk again with someone else’s -f option to make sure it changes They were recorded on disc. You can mount your newborn on a partition using “mount” get.
Can you format to FAT32?
Enter [This PC] in all Windows search boxes ① and click [Open] ②. Right-click USB storage ③, select [Format] ④. Select the file system to change to [FAT32] ⑤, then click [Start] ⑥. Click [OK] ⑦ to start formatting the USB stick.
How do I force a FAT32 format?
Click on the Start Menu.Click This PC.Right click on the USB stick.Click Format.Click Start. If the file system is not marked as FAT32, click the drop-down menu and select it.Click OK.Wait for the drive to be formatted and then click OK to complete the process.
Linux Formatteren Fat32
Formatacao Linux Fat32
Formattazione Linux Fat32
Linux Formatowanie Tluszczu32
Linux Formatierung Fat32
Linux Formatear Fat32
Formatage Linux Fat32
Linux Formatering Fat32
Linuks Formatiruet Fat32
리눅스 포맷 Fat32